Lower Back Pain
- Home
- »
- Treatments
- »
- Lower Back Pain
LOW BACK PAIN (LBP) is a pandemic disease having 80% of lifetime prevalence, affecting 15-20% population at any point of time, being one of the commonest reason for visit to a doctor & young age morbidity/disability/work absenteeism.
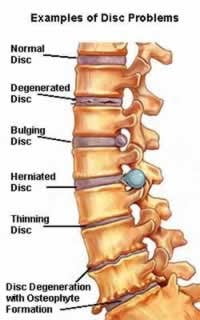
Some of the main causes of back pain include facet arthropathy, sciatica, muscle strain, sacroilitis, bulging or herniated discs and degenerative disc disease. Prolapsed intervertebral discs (PIVD) are the most common cause of low back pain associated with a defined structural Abnormality.
While spinal arthritis is the common reason of young age back pain at prime of their carriers including some bollywood celebrities, disc diseases including slip disc is prevalent in all age groups, in young age due to trauma & in old age due to degeneration.
Patients who are not helped by weeks of conservative therapy are often referred for surgery on the premise that further non-operative care is unlikely to help. Ideally, a patient with low back pain that has persisted beyond a four-week period should be referred to a multidisciplinary pain centre. With interventional pain management patients are getting back to life. It has both diagnostic and treatment values, as sometimes all investigations put together do not give the exact diagnosis.
ONCE THE CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT FAILS:-
Early aggressive treatment plan of pain has to be implemented to prevent peripherally induced CNS changes that may intensify or prolong pain making it a complex pain syndrome. Only 5% of total LBP patients would need surgery & 20% of discal rupture or herniation would need surgery. Nonoperative treatment is sufficient in most of the patients, although patient selection is important even then.
Depending upon the diagnosis one can perform & combine properly selected percutaneous fluoroscopic guided procedures with time spacing depending upon pt`s pathology & response to treatment.
Using precision diagnostic & therapeutic blocks in chronic LBP , isolated facet joint pain in 40%, discogenic pain in 25%(95% in L4-5&L5S1) ,segmental dural or nerve root pain in 14% & sacroiliac joint pain in 15% of the patients. This article describes successful interventions of these common causes of LBP after conservative treatment has failed.
Different Non Surgical Interventions Employed Successfully:
Epidural Steroid Inj.
Nerve root sleeve/ transforaminal Inj.
Epidurogram & Epidurolysis.
Nucleoplasty- Laser, Drill, RF decompression
Ozone Discolysis
Facet Joint Block & RF Denervation
SI Joint Block
Newer technologies like ozone injection cures most of the patients of slip disc & sciatica, as ozone’s nascent oxygen atom shrinks the disc so taking away pressure from pain sensitive nerves. It is a non surgical, outpatient procedure done under local anesthesia not requiring bed rest for more than day or two & prolonged absence from work realizing the importance of time, at much lower cost with almost no complications. This procedure is done under radiological guidance for precise needle targeting and best results. There after patient is given advice for spine care & healthy habits. This technology is latest & many people including medical caregivers don’t know about it. It has benefited millions in developed world and is now available in India also.
Piriformis Syndrome
Piriformis syndrome is a neuromuscular disorder that occurs when the sciatic nerve is compressed or otherwise irritated by the piriformis muscle causing pain, tingling and numbness in the buttocks and along the path of the sciatic nerve descending down the lower thigh and into the leg. Diagnosis is often difficult due to few validated and standardized diagnostic tests, but one of the most important criteria is to exclude sciatica resulting from compression/irritation of spinal nerve roots, as by a herniated disk. The syndrome may be due to anatomical variations in the muscle-nerve relationship, or from overuse or strain. Piriformis syndrome should be considered as a possible diagnosis when Sciatica occurs without a clear spinal cause.
TREATMENT
Symptomatic relief of muscle and nerve pain can be obtained by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and/or muscle relaxants. Conservative treatment usually begins with stretching exercises and massage, and avoidance of contributory activities, such as running, bicycling, rowing, etc. Some clinicians recommend formal physical therapy, Failure of conservative treatments described above may lead to consideration of various therapeutic injections such as local anesthetics, Anti-inflammatory drugs and/or corticosteroids, botulinum toxin (BOTOX), or a combination of the three. Injection technique is a significant issue since the piriformis is a very deep seated muscle. BOTOX can be injected under CT control. This inactivates the piriformis muscle for 3 to 6 months, without resulting in leg weakness or impaired activity. Rarely surgery may be recommended.
THE MANAGEMENT OF INTRACTABLE- LOW BACK PAIN : RECENT ADVANCES
DR. NEERAJ JAIN
Interventional Pain Specialist ,Spine & Pain Clinic. RU-23 Pitampura,
& Consultant Incharge, Pain Clinic, Sri Balaji Action Medical Institute, New Delhi,
& Max Hospital, Delhi.
[email protected], 9810033800 (Mobile). www.spinenpain.com
LOW BACK PAIN (LBP) is a pandemic disease having 80% of lifetime prevalence, affecting 15-20% population at any point of time, being one of the commonest reason for visit to a doctor & young age morbidity/disability/work absenteeism.
AETIOLOGY OF LBP:
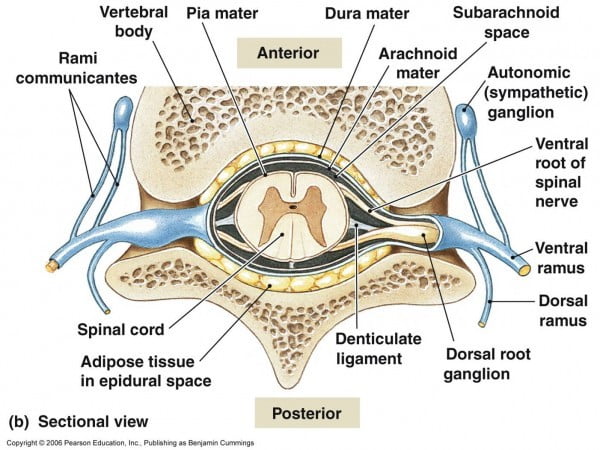
LBP is not just a disease but a symptom, a syndrome with combination of multiple possible abnormalities of anterior & posterior longitudinal ligaments, vertebral body, synovia / chondropathy/ osteoarthritis of articulating facets joints, sacroiliac joint, nerve roots & foramen, paraspinal muscles, related connective tissues eg.- ligamentum flavum , spinal canal, intervetebral disc at annulus ring. It may be due to mechanical, nonmechanical, referred pain, psychological & failed back surgery (FBSS).
PERCUTANEOUS LEAST INVASIVE INTERVENTIONAL
PAIN MANAGEMENT OF LBP:-
It has both diagnostic & therapeutic relevance( as there are significant false positive & negative imaging studies not correlating to symptoms)
Better results are obtained if treatment is started early.
- LESI-lumbar epidural steroid injections::
- interlamminar or transforaminal or caudal approach
- SNRB- selective nerve root block
- Epidural adenolysis or percutaneous decompressive neuroplasty
- Trigger point injection
- Botox paraspinal muscle injection
- Facet joint or pericapsular injection
- Spine Prolotherapy & manipulation
- Facet RF thermal neurolysis
- SI joint injection or denervation
- Piriformis muscle block
- Diagnostic provocative discography
- Intradiscal procedures:-Ozone Discolysis/ Chemonucleolysis
- Dekompressor disc debulking
- IDET-intradiscal electrothermal therapy
- Coblation nucleoplasty
- Laser percutaneous discectomy
- Vertebroplasty & kyphoplasty
- Intrathecal pump neuraxial implants
- Augmentation or neuromodulation spinal cord stimulation
ONCE THE CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT FAILS:-
Early aggressive treatment plan of pain has to be implemented to prevent peripherally induced CNS changes that may intensify or prolong pain making it a complex pain syndrome. Only 5% of total LBP patients would need surgery & 20% of discal rupture or herniation would need surgery. Nonoperative treatment is sufficient in most of the patients, although patient selection is important even then.
Depending upon the diagnosis one can perform & combine properly selected percutaneous fluoroscopic guided procedures with time spacing depending upon pt`s pathology & response to treatment.
Using precision diagnostic & therapeutic blocks in chronic LBP , isolated facet joint pain in 40%, discogenic pain in 25%(95% in L4-5&L5S1) ,segmental dural or nerve root pain in 14% & sacroiliac joint pain in 15% of the patients. This article describes successful interventions of these common causes of LBP after conservative treatment has failed
LESI : LUMBAR EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION
Indicated in – Acute radicular pain due to irritation or inflammation.
- Symptomatic herniated disc with failed conservative therapy
- Acute exerbation of discogenic pain or pain of spinal stenosis
- Neoplastic infiteration of roots
- Epidural fibrosis
- Chronic LBP with acute radicular symptoms
ESI TREATMENT PLAN:
Compared to interlaminar approach better results are found with transforaminal approach where drugs (steroid+ LA/saline +/- hyalase) are injected into anterior epidural space & neural foramen area where herniated disc or offending nociceptors are located. Whereas in interlaminar approach most of drug is deposited in posterior epidural space.Drugs are injected total 6-10 ml at lumbar, 3-6 ml at cervical & 20+ ml if caudal approach is selected. Lumbar ESI is performed close to the level of radiculopathy, often using paramedian approach to target the lateral aspect of the epidural space on involved side. Cervical epidural is performed at C7-T1 level .
SNRB- SELECTIVE NERVE ROOT BLOCK.
Fluoroscopically performed it is a good diagnostic & therapeutic procedure for radiculopathy pain if
- There is minimal or no radiological finding.
- Equivocal neurological examination finding or discrepancy between clinical & radiological signs
- Postop patient with unexplainable or recurrent pain
- Combined canal & lateral recess stenosis.
- To find out the pathological dermatome for more invasive procedures , if needed
EPIDURAL ADENOLYSIS OR PERCUTANEOUS DECOMPRESSIVE
NEUROPLASTY for EPIDURAL FIBROSIS OR ADHESIONS IN FAILED BACK SURGERY SYNDROMES (FBSS)
A catheter is inserted in epidural space via caudal/ interlaminar/ transforaminal approach
After epidurography testing volumetric irrigation with normal saline/ L.A./ hyalase/ steroids/ hypertonic saline in different combinations is then performed along with
mechanical adenolysis with spring loaded or stellated catheters or under direct vision with EPIDUROSCOPE
FACET SYNDROME:- FACET JOINT INJECTION OR
RF MEDIAL BRANCH NEUROTOMY
It is due to mechanical stress on the Zygapophysial joints or traumatic/anatomical derangement & degenerative facet arthropathy. It is commoner in male of younger age group during active careers . CT/ MRI/ Bone scan show structural pathology, but diagnosis is confirmed by relief of pain with joint injection (1ml of LA+ 20 mg triamcinolone) which has therapeutic value also.After effective facet joint block, fluoroscopic percutaneous radiofrequency(RF) thermal rhizotomy of two level medial branches of dorsal ramus is a safe, effective & long term treatment.
SACROILIAC JOINT INJECTION & DENERVATION:
The only way to make a definitive diagnosis is pain relief with image guided joint injection of depo-steroid with L.A..This can be followed by joint denervation of L4-5 S1-3 branches to this joint providing long term pain relief.
INTRADISCAL PROCEDURES::
PROVOCATIVE DISCOGRAPHY: coupled with CT
A diagnostic procedure & prognostic indicator for surgical outcome is necessary in the evaluation of patients with suspected discogenic pain, its ability to reproduce pain(even with normal radiological finding), to determine type of disc herniation /tear, finding surgical options & in assessing previously operated spines
PERCUTANEOUS DISC DECOMPRESSION (PDD)
After diagnosing the level of painful offending disc various percutaneous intradiscal procedures can be employed:–
OZONE-DISCOLYSIS:
Ozone Discectomy a revolutionary least invasive safe & effective alternative to spine surgery is the treatment of choice for prolapsed disc (PIVD) done under local anaesthesia in a day care setting. This procedure is ideally suited for cervical & lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy. Total cost of the procedure is much less than that of surgical discectomy. All these facts have made this procedure very popular at European countries. It is also gaining popularity in our country due to high success rate, less invasiveness, fewer chances of recurrences, remarkably fewer side effects meaning high safety profile, short hospital stay, no post operative discomfort or morbidity and low cost.
DEKOMPRESSOR:
A mechanical percutaneous nucleotome cuts & drills out the disc material somewhat like morcirator debulking the disc reducing nerve compression
INTRATHECAL (SPINAL) PUMP IMPLANTS:
Opted when oral narcotics provide insufficient pain relief or side effects are troublesome in intractable cancer & chronic pain patients. It delivers drug via an implanted catheter directly into CSF needing a very small dose (1/300 of oral dose). The programmable pump is implanted in ant. lower abdomen. It delivers the drug as per the patients needs. More powerful analgesia & spasticity control is achieved using lower doses, constant relief & fewer side effects as with oral doses eg. Somnolence, mental clouding, constipation, euphoria with decreased chances of drug addiction or misuse.
NEUROMODULATION TECHNIQUES:
SPINAL CORD STIMULATION (SCS) IMPLANTS :
Done for FBSS( failed back surgery syndrome) & CRPS(comlex regional pain syndromes) inUSA. In Europe it is done for chronic intractable angina & pain of peripheral vascular diseases (PVD). The indications are expanding further in chronic pain states. A set of electrodes is placed in epidural space & connected to a pulse generator ( like a cardiac pacing device) that is implanted in upper buttock. Low level of electric impulses replace pain signals to the brain with mild tingling sensation. A trial stimulation is done before permanent SCS lead implant
PERCUTANEOUS VERTEBROPLASTY / KYPHOPLASTY:
A NEWER APPROACH TO MANAGEMENT OF VERTEBRAL BODY FRACTURES
As life expectancy is increasing so is the incidence of vertebral body (VB) # now being the commonest # of the body. PVP is an established interventional techniques in which PMMA bone cement is injected under L.A. via a needle into a # VB with imaging guidance providing increased bone strength, stability, pain relief, decreased analgesics, increased mobility with improved QOL and early return to work
The Management of Intractable Low Back Pain: Recent Advances
Neeraj Jain, Ashok Jain*
Senior Consultant Spine & Pain Specialist, Spine & Pain Clinics & Sri Balaji Action Medical Institute,
Max Hospital, Pitampura, New Delhi & Sant Parmanand Hospital, New Delhi, India
*Diplomate in American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology, General Psychiatry, Diplomate in American Board
of Psychiatry and Neurology, Pain Medicine, Diplomate in American Board of Disability Analyst
Psychiatric Solutions PC, 1201 Creek Way Drive, Suite C, Sugar Land Texas, USA
Abstract: Low back pain (LBP) a pandemic disease having 80% of lifetime prevalence, affecting 15-20% population at any point of time, being one of the commonest reason for visit to a doctor(as such pain is the commonest reason to see a doctor) &commonest cause of young age disability (3-4% annually with 1% permanently disabled).30% of all acute LBP develop chronic LBP. It has great financial, socioeconomic, emotional & physical problem. Percutaneous least invasive interventional Pain management of LBP has both diagnostic & therapeutic relevance (as there are significant false positive & negative imaging studies not correlating to symptoms). Better results are obtained if treatment is started early. “No one needs to suffer as so many good and effective treatments are now available at specialty pain clinics”. You must see a pain specialist if you still suffer from pain after a month of conservative treatment. Sooner your pain is managed better are the overall results. With interventional pain management patients are getting back to normal life.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
LOW BACK PAIN (LBP) is a pandemic disease having 80% of lifetime prevalence, affecting 15-20% population at any point of time, being one of the commonest reason for visit to a doctor & young age morbidity disability/work absenteeism.
AETIOLOGY OF LBP
LBP is not just a disease but a symptom, a syndrome with combination of multiple possible abnormalities of anterior & posterior longitudinal ligaments, vertebral body, synovia / chondropathy/ osteoarthritis of
articulating facets joints, sacroiliac joint, nerve roots & foramen,paraspinal muscles, related connective tissues eg.- ligamentum flavum , spinal canal, intervetebral disc at annulus ring. It may be due to mechanical, nonmechanical, referred pain, psychological & failed back surgery (FBSS).
PERCUTANEOUS LEAST INVASIVE
INTERVENTIONAL PAIN MANAGEMENT OF LBP
It has both diagnostic & therapeutic relevance( as there are significant false positive & negative imaging studies not correlating to symptoms) Better results are obtained if treatment is started early.
- LESI-lumbar epidural steroid injections::
- interlamminar or transforaminal or caudal approach
- SNRB- selective nerve root block
- Epidural adenolysis or percutaneous decompressive neuroplasty
- Trigger point injection
- Botox paraspinal muscle injection
- Facet joint or pericapsular injection
- Spine Prolotherapy & manipulation
- Facet RF thermal neurolysis
- SI joint injection or denervation
- Piriformis muscle block
- Diagnostic provocative discography
- Intradiscal procedures:-Ozone Discolysis/ Chemonucleolysis
- Dekompressor disc debulking
- IDET-intradiscal electrothermal therapy
- Coblation nucleoplasty
- Laser percutaneous discectomy
- Vertebroplasty & kyphoplasty
- Intrathecal pump neuraxial implants
Correspondence: Dr Neeraj Jain, Senior Consultant Spine & Pain Specialist, Spine & Pain Clinics & Sri Balaji Action Medical Institute, Max Hospital, Pitampura, New Delhi & Sant Parmanand Hospital, NewDelhi. e-mail: [email protected] www.spinenpain.com
Augmentation or neuromodulation spinal cord stimulation
Once The Conservative Treatment Fails
Early aggressive treatment plan of pain has to be implemented to prevent peripherally induced CNS changes that may intensify or prolong pain making it a complex pain syndrome. Only 5% of total LBP patients would need surgery & 20% of discal rupture or herniation would need surgery. Nonoperative treatment is sufficient in most of the patients, althoughpatient selection is important even then. Depending upon the diagnosis one can perform & combine properly selected percutaneous fluoroscopic guided procedures with time spacing depending upon patients pathology & response to treatment. Using precision diagnostic & therapeutic blocks in chronic LBP , isolated facet joint pain in 40%, discogenic pain in 25%(95% in L4-5&L5S1) , segmental dural or nerve root pain in 14% & sacroiliac joint pain in 15% of the patients. This article describes successful interventions of these common causes of LBP after conservative treatment has failed.
LESI : Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injection
Indications
- Acute radicular pain due to irritation or inflammation.
- Symptomatic herniated disc with failed conservative therapy
- Acute exerbation of discogenic pain or pain of spinal stenosis
- Neoplastic infiteration of roots
- Epidural fibrosis
- Chronic LBP with acute radicular symptoms
ESI Treatment Plan
Compared to interlaminar approach better results are found with transforaminal approach where drugs (steroid+ LA/saline +/- hyalase) are injected into anterior epidural space & neural foramen area where herniated disc or offending nociceptors are located. Whereas in interlaminar approach most of drug is deposited in posterior epidural space.Drugs are injected total 6-10 ml at lumbar, 3-6 ml at cervical & 20+ ml if caudal approach is selected. Lumbar ESI is performed close to the level of radiculopathy, often using paramedian approach to target thelateral aspect of the epidural space on involved side. Cervical epidural isperformed at C7-T1 level.
SNRB- Selective Nerve Root Block
Fluoroscopically performed it is a good diagnostic & therapeutic procedure for radiculopathy pain if
- There is minimal or no radiological finding.
- Multilevel imaging abnormalities
- Equivocal neurological examination finding or discrepancy between
clinical & radiological signs - Postop patient with unexplainable or recurrent pain
- Combined canal & lateral recess stenosis.
- To find out the pathological dermatome for more invasive procedures, if needed
Epidural adenolysis or percutaneous decompressive neuroplasty for epidural fibrosis or adhesions in failed back surgery syndromes (FBSS)
A catheter is inserted in epidural space via caudal/ interlaminar/ transforaminal approach After epidurography testing volumetric irrigation with normal saline/ L.A./ hyalase/ steroids/ hypertonic saline in different combinations is then performed along with mechanical adenolysis with spring loaded or stellated catheters or under direct vision with EPIDUROSCOPE.
Facet Syndrome: Facet Joint Injection or RF Medial Branch Neurotomy
It is due to mechanical stress on the Zygapophysial joints or traumatic/ anatomical derangement & degenerative facet arthropathy. It is commoner in male of younger age group during active careers . CT/ MRI/ Bone scan show structural pathology, but diagnosis is confirmed by relief of pain with joint injection (1ml of LA+ 20 mg triamcinolone) which has therapeutic value also.After effective facet joint block, fluoroscopic percutaneous radiofrequency(RF) thermal rhizotomy of two level medial
branches of dorsal ramus is a safe, effective & long term treatment.
Sacroiliac Joint Injection & Denervation
The only way to make a definitive diagnosis is pain relief with image guided joint injection of depo-steroid with L.A..This can be followed by joint denervation of L4-5 S1-3 branches to this joint providing long term pain relief.
INTRADISCAL PROCEDURES
Provocative Discography: Coupled with CT
A diagnostic procedure & prognostic indicator for surgical outcome is necessary in the evaluation of patients with suspected discogenic pain, its ability to reproduce pain(even with normal radiological finding), to determine type of disc herniation /tear, finding surgical options & in assessing previously operated spines
Percutaneous Disc Decompression (PDD)
After diagnosing the level of painful offending disc various percutaneous intradiscal procedures can be employed.
Ozone-Discolysis
Ozone Discectomy a revolutionary least invasive safe & effective alternative to spine surgery is the treatment of choice for prolapsed disc (PIVD) done under local anaesthesia in a day care setting. This procedure is ideally suited for cervical & lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy. Total cost of the procedure is much less than that of surgical discectomy. All these facts have made this procedure very popular at European countries. It is also gaining popularity in our country due to high success rate, less invasiveness, fewer chances of recurrences, remarkably fewer side effects meaning high safety profile, short hospital stay, no postoperative discomfort or morbidity and low cost.
Dekompressor
A mechanical percutaneous nucleotome cuts & drills out the disc material somewhat like morcirator debulking the disc reducing nerve compression.
Intrathecal (Spinal) Pump Implants
Opted when oral narcotics provide insufficient pain relief or side effects are troublesome in intractable cancer & chronic pain patients. It delivers drug via an implanted catheter directly into CSF needing a very small dose (1/300 of oral dose). The programmable pump is implanted in ant. lower abdomen. It delivers the drug as per the patients needs. More powerful analgesia & spasticity control is achieved using lower doses, constant relief & fewer side effects as with oral doses eg. Somnolence, mental clouding, constipation, euphoria with decreased chances of drug addiction or misuse
NEUROMODULATION TECHNIQUES
Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS) Implants
Done for FBSS( failed back surgery syndrome) & CRPS(comlex regional pain syndromes) inUSA. In Europe it is done for chronic intractable angina & pain of peripheral vascular diseases (PVD). The indications are expanding further in chronic pain states. A set of electrodes is placed in epidural space & connected to a pulse generator ( like a cardiac pacing device) that is implanted in upper buttock. Low level of electric impulsesreplace pain signals to the brain with mild tingling sensation. A trial stimulation is done before permanent SCS lead implant.
PERCUTANEOUS VERTEBROPLASTY / KYPHOPLASTY
A Newer Approach To Management Of Vertebral Body Fractures
As life expectancy is increasing so is the incidence of vertebral body (VB) # now being the commonest # of the body. PVP is an established interventional techniques in which PMMA bone cement is injected under L.A. via a needle into a # VB with imaging guidance providing increased bone strength, stability, pain relief, decreased analgesics, increased mobility with improved QOL and early return to work.
PIRIFORMIS SYNDROME
Piriformis syndrome is a neuromuscular disorder that occurs when the sciatic nerve is compressed or otherwise irritated by the piriformis muscle causing pain, tingling and numbness in the buttocks and along the path of the sciatic nerve descending down the lower thigh and into the leg. Diagnosis is often difficult due to few validated and standardized diagnostic tests, but one of the most important criteria is to exclude sciatica resulting from compression/irritation of spinal nerve roots, as by a herniated disk. The syndrome may be due to anatomical variations in the muscle-nerve relationship, or from overuse or strain. Piriformis syndrome should be considered as a possible diagnosis when Sciatica occurs without a clear spinal cause
Treatment
Symptomatic relief of muscle and nerve pain can be obtained by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and/or muscle relaxants. Conservative treatment usually begins with stretching exercises and massage, and avoidance of contributory activities, such as running, bicycling, rowing, etc. Some clinicians recommend formal physical therapy, Failure ofconservative treatments described above may lead to consideration ofvarious therapeutic injections such as local anesthetics, Anti-inflammatorydrugs and/or corticosteroids, botulinum toxin (BOTOX), or a combination of the three. Injection technique is a significant issue since the piriformis is a very deep seated muscle. BOTOX can be injected under CT control. This inactivates the piriformis muscle for 3 to 6 months, without resulting in leg weakness or impaired activity. Rarely surgery may be recommended.
COCCYDYNIA/TAIL BONE PAIN
Coccyx pain is often caused by falling backwards or by childbirth, though the cause of pain is unknown in about a third of cases. It makes it very painful to sit down. There are effective treatments available, and the great majority of sufferers can be cured. Most coccyx pain is caused by the coccyx dislocating when you sit. In such cases, manual treatments, if applied by an expert, may relieve the pain. Injections of cortisone help some people.
Coccydynia is often reported following a fall or after childbirth. In some cases, persistent pressure from activities like bicycling may cause the onset of coccyx pain. Coccydynia due to these causes usually is not permanent, but it may become very persistent and chronic if not controlled. Activities that put pressure on the affected area are bicycling, horseback riding, and other activities such as increased sitting that put direct stress on the coccyx. The medical condition is often characterized by pain that worsens with constipation and may be relieved with bowel movement. Activities that put pressure on the affected area are bicycling, horseback riding, and other activities such as increased sitting that put direct stress on the coccyx. The medical condition is often characterized by pain that worsens with constipation and may be relieved with bowel movement. ometimes even just a single local nerve block injection at the ganglion impar can give 100% relief of coccydynia when performed under fluoroscopic guidance.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
- An Algorithmic Approach for Clinical Management of Chronic Spinal Pain ASIPP – EBM Guidelines 2009, Ref-Pain Physician 2009; 12:E225-E264
- Carragee E, Lincoln T, Parmar V, Alamin T, Carragee J. A gold standard evaluation of the “discogenic pain” diagnosis as determined by provocative discography. Spine 2005.
- Cassidy JD, Carroll LJ, Cote P. The Saskatchewan Health and Back Pain Survey: the prevalence of low back pain and related disability in Saskatchewan adults. Spine 1998;23:1860-66.
- Carragee E, Cohen S. Reliability of LBP history in asymptomatic subjects? The prevalence and incidence of reported back pain correlates with surveillance frequency. In: Proceedings of the 19th Annual Meeting of the North American Spine Society, Chicago, October 26–30, 2004:216. abstract.
- Dreyfuss P, Halbrook B, Pauza K, Joshi A, McLarty J, Bogduk N. Efficacy and validity of radiofrequency neurotomy for chronic lumbar zygapophysial joint pain. Spine 2000;25:1270-7.
- Skovron ML, Szpalski M, Nordin M, Melot C, Cukier D. Sociocultural factors and back pain: a population-based study in Belgian adults. Spine 1994;19:129-37.
- van Kleef M, Weber WE, Kessels A,Dreyfuss P, Pauza K, Bogduk N. Re: Efficacy and validity of radiofrequency neurotomy for chronic lumbar zygapophysial joint pain (Spine 2000;25:1270-7). Spine 2001;26: E163-4.
Next Issue Highlights
- Thyroid Nodule: Diagnostic & Therapeutic Challenges
- Hernia Repair : Challenges & Innovations
- Clinical Drug Interaction
- Symposium: Interesting Clinical Problems in Dermatology

